What is Bloating?
Bloating is the subjective sensation of increased abdominal pressure, tightness, or fullness. It is often accompanied by abdominal distension, which is a visible, measurable increase in the size of your stomach (girth).
While many people equate bloating with "excess gas," they are not always the same. You can feel severely bloated even with a normal amount of gas if your gut is hypersensitive. When bloating occurs frequently—at least one day per week for three months—without significant pain or changes in bowel habits, doctors may diagnose it as Functional Bloating.
Causes of Bloating
The causes of bloating are multifactorial, involving how your body processes food, air, and waste.
-
Dietary Triggers (FODMAPs): The most common trigger. These are fermentable carbohydrates (like those in onions, garlic, apples, and beans) that the gut has trouble absorbing, leading to fermentation and gas production.
-
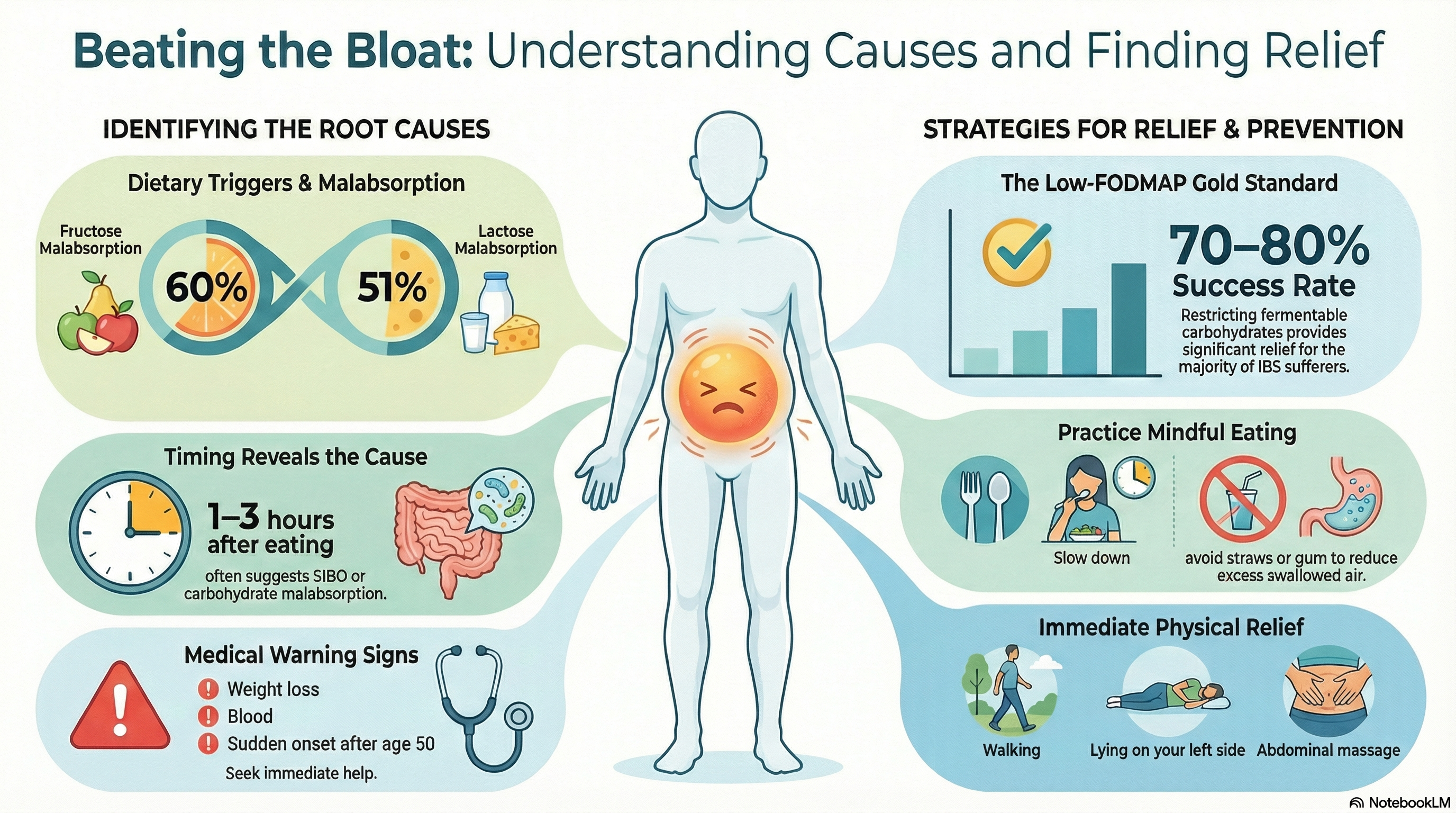
Malabsorption: Up to 60% of people with chronic bloating have difficulty absorbing fructose, and 51% struggle with lactose (dairy).
-
Swallowed Air (Aerophagia): Eating too fast, chewing gum, smoking, or drinking carbonated beverages introduces excess air into the digestive tract.
-
Constipation: When stool moves slowly, it has more time to ferment, which generates gas and pressure.
-
Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO): An imbalance where excessive bacteria in the small intestine ferment food too early in the digestive process.
-
Gut-Brain Interaction: In conditions like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), the nerves in the gut are hypersensitive, making normal gas levels feel painful or bloated.
-
Hormonal Changes: Many women experience bloating during the premenstrual phase, pregnancy, or menopause due to fluctuations in progesterone.
Symptoms of Bloating
Symptoms vary based on the underlying cause but generally include:
-
Fullness and Pressure: A feeling that your stomach is "stuffed," even after a small meal.
-
Visible Swelling: Noticing that your clothes fit tighter as the day progresses.
-
Trapped Gas: A feeling of air "stuck" in the abdomen that is difficult to pass.
-
Timing Clues: * Immediate bloating: Often due to swallowed air or delayed stomach emptying.
-
1–3 hours after eating: Often suggests SIBO or carbohydrate malabsorption.
-
Evening worsening: Typical of dietary fermentation throughout the day.
-
Warning Signs: See a doctor immediately if bloating is accompanied by unexplained weight loss (>10%), blood in the stool, persistent vomiting, or if it starts suddenly after the age of 50.
Diagnosis of Bloating
Diagnosis typically begins with a physical exam and a review of your symptoms.
-
Clinical Evaluation: Doctors use the "Rome IV criteria" to identify functional bloating based on the frequency and duration of your symptoms.
-
Physical Exam: A doctor may tap on your abdomen (tympany) or check for abnormal bowel sounds or masses.
-
Breath Testing: Used to identify lactose/fructose malabsorption or SIBO.
-
Elimination Diet: Tracking symptoms while removing certain food groups to pinpoint triggers.
-
Imaging and Endoscopy: Usually reserved for "red flag" cases where there is a concern about inflammation, obstruction, or malignancy.
Treatment of Bloating
There is no "magic pill," but a combination of strategies usually provides significant relief.
-
Dietary Management: The Low-FODMAP diet is the gold standard for many, showing a 70–80% success rate for those with IBS or SIBO. Restricting lactose or fructose can also be highly effective.
-
Probiotics: Specific strains like Bifidobacterium infantis are well-studied for reducing bloating and balancing the microbiome.
-
Natural Remedies: Enteric-coated peppermint oil helps relax the muscles of the gut, while ginger can speed up stomach emptying.
-
Physical Activity: A 20–30 minute walk after meals is clinically shown to help the gut move gas along more efficiently.
-
Medications: Over-the-counter options like simethicone help break up gas bubbles. For SIBO, a doctor may prescribe an antibiotic like Rifaximin.
-
Quick Relief: Lying on your left side, applying a heating pad, or performing a clockwise abdominal massage can help move trapped gas.
Prevention of Bloating
Long-term management focuses on preventing the buildup of gas and maintaining gut motility.
-
Eat Mindfully: Slow down while eating and avoid talking during meals to reduce the amount of air you swallow.
-
Identify Your Triggers: Keep a food diary to see if specific artificial sweeteners (like sorbitol or xylitol) or high-fiber foods are causing your issues.
-
Aggressively Treat Constipation: Ensure you are hydrated and consuming adequate (but not excessive) fiber to keep your system moving.
-
Avoid Irritants: Minimize carbonated drinks, chewing gum, and using straws.
-
Stress Management: Since the gut and brain are closely linked, practices like yoga or mindfulness can reduce the visceral hypersensitivity that makes bloating feel worse.





